The discovery of 20,000-year-old pottery fragments in a Chinese cave has transformed our comprehension of early human creativity. Much older than any previously discovered pottery examples, these containers have questioned the traditional belief that pottery and farming emerged together. Research on ancient pottery has revealed the resourcefulness of foraging communities well before they started cultivating crops, as highlighted in key publications such as those released inScience and Documenta Praehistorica.
The Earliest Ceramics: A Revolution in Understanding Ancient Times
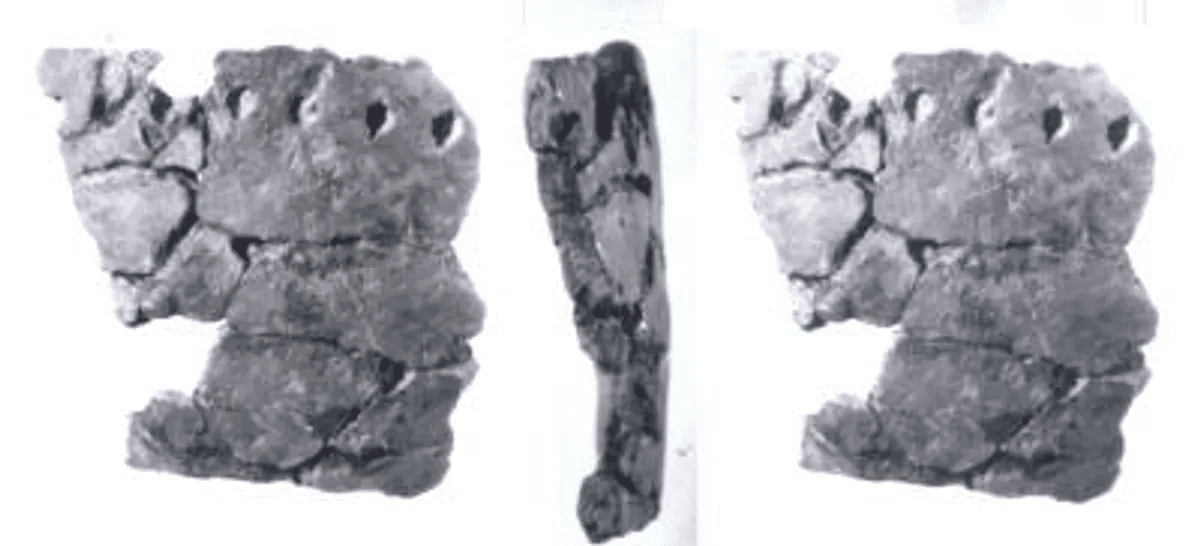
In 2012, researchers unearthed pottery fragments in a cavePottery found in China, which has been dated to between 19,000 and 20,000 years ago, makes them the oldest pottery ever discovered. “The radiocarbon dates of the archaeological layers where the earliest fragments were found range from 20,000 to 19,000 calendar years ago, being 2000 to 3000 years older than other pottery found in East Asia and other regions,” stated the researchers in their pioneering study. This finding significantly changes our understanding of technological development, showing that early humans were making pottery long before the start of agriculture.
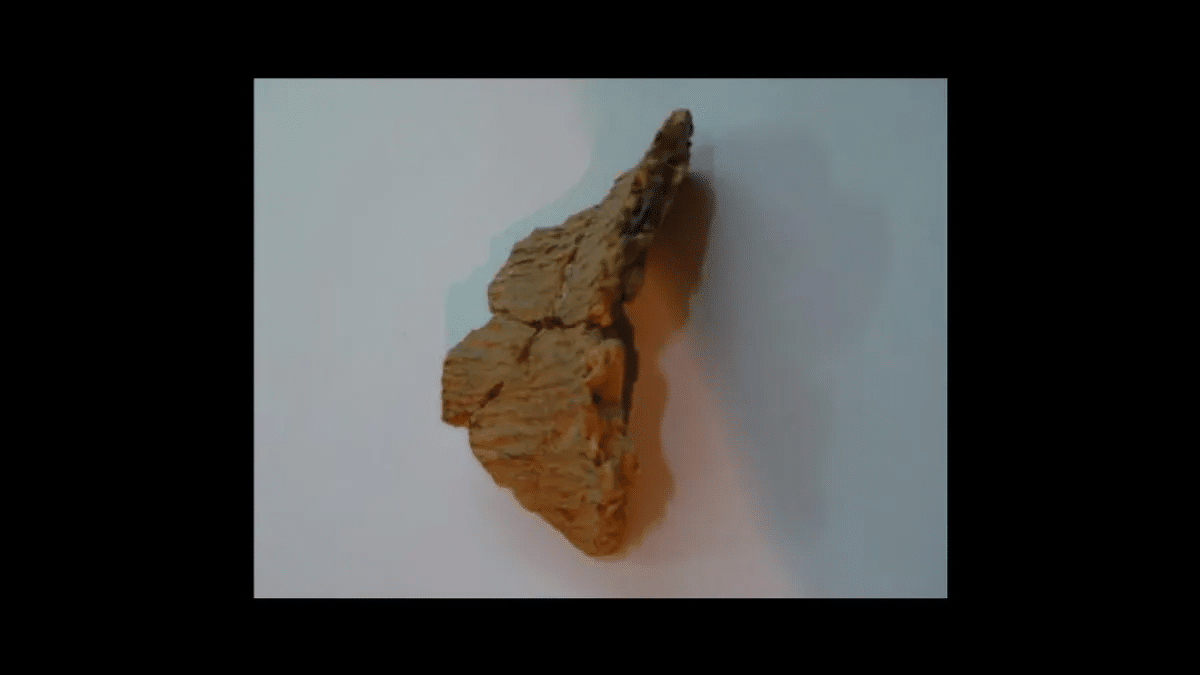

The significance of these results is substantial. The cave settlements, as outlined by the research group, indicate that these ancient containers were created by nomadic foragers who hunted and collected during the Late Glacial Maximum. These containers were probably utilized for cooking, offering important information about how our predecessors may have adjusted to the difficult circumstances of that time. “The early dating indicates that pottery was created and used 10,000 years or more before the rise of agriculture,” the researchers stated. This contradicts earlier beliefs that pottery developed only after the beginning of farming and settled ways of life.
The Significance of Ceramics in Ancient Human Cultures
Pottery was not only a technological advancement; it also had a major impact on social interactions. Although people often link early human progress with farming and food cultivation, this finding indicates that hunter-gatherersThey were already using sophisticated tools like pottery to enhance their everyday living. These early pots could have been employed to prepare high-trophic-level aquatic foods, including fish, shellfish, and possibly snails, as indicated by findings from relevant research.
By analyzing minute traces discovered on comparablepottery fragmentsResearchers have proposed that these containers were utilized for more than just heating water. Some believe they could have had a wider social function, such as boiling animal bones to extract fat or even producing early versions of alcoholic beverages. This would not only meet practical requirements but also contribute to ritualistic feasts, an essential aspect of early societies. As geoarchaeologist Yaroslav V. Kuzmin stated, “The development of pottery is one of the most significant events in prehistory.” It may have been crucial in assisting these early East Asians in adapting to major climatic shifts during that period.
The Influence of Climate and Tradition on the Evolution of Pottery
One of the most remarkable features of this finding is its connection to the changing climateduring the Late Glacial Maximum. The adoption of pottery probably enabled ancient humans to more effectively manage changing environmental circumstances. These early potters were not yet agriculturalists, but they were skilled in utilizing existing resources to make tools that aided their survival. This is evident in the wide range of functions pottery served, from cooking and brewing to participation in social events.
As the climate shifted, early humanshad to adjust rapidly to changing circumstances, with pottery possibly playing a key role in this flexibility. Indeed, the development of these containers might have represented a significant shift in how ancient communities engaged with their surroundings. The significance of pottery in this regard is hard to overemphasize, as it enabled early humans to store, prepare, and keep food in methods that had not been feasible before. The finding of these early pottery pieces indicates that, even prior to the start of farming, people were already creating technologies that would lay the groundwork for later civilizations.
Enjoyed this article? Sign up for our free Newsletterfor captivating narratives, unique material, and up-to-the-minute updates
For additional news similar to this, visitIndiandefencereview.com






Leave a comment