China has officially initiated a shift away from “NVIDIA” by prohibiting the use of semiconductors developed specifically for the Chinese market by NVIDIA. This move is seen as encouraging domestic semiconductor firms to enhance their technological expertise and showcasing belief in achieving dominance in the tech sector without relying on U.S.-made chips.
The UK’s Financial Times (FT) reported on the 17th (local time) that China’s Cyberspace Administration (CAC) recently directed Chinese technology companies, including ByteDance and Alibaba, to stop placing orders and conducting tests with NVIDIA’s “RTX 6000D” chip. It is understood that Chinese firms that had already placed large orders and were testing the chip have now halted all related activities. The RTX 6000D is a graphics processing unit (GPU) that NVIDIA designed specifically for the Chinese market. The technology sector sees the Chinese authorities’ restriction on importing NVIDIA chips as a further step toward semiconductor self-sufficiency. NVIDIA GPUs hold more than 80% of the global market share and are crucial for AI training and data center operations. A source in the tech industry said, “The Trump administration’s continuous sanctions against China have sped up the country’s move toward semiconductor independence, causing unintended damage to U.S. and allied semiconductor companies.”
◇China’s Assurance in Domestic AI Chip Development
In reaction to U.S. restrictions on semiconductors, China has concentrated on supporting local semiconductor companies. In 2024, it created a 344 billion yuan (67 trillion Korean won) investment fund for the semiconductor sector—the third major investment after 2014 (138.7 billion yuan) and 2019 (204 billion yuan). By injecting substantial capital into promising enterprises, it quickly enhanced technological development. Especially, with the U.S. prohibiting the export of advanced semiconductor chips and machinery, China sped up its localization efforts to address the shortfall.
It has been reported that Chinese officials carried out targeted testing of NVIDIA’s RTX chips and found them capable of being substituted with local alternatives. The Financial Times noted, “Chinese authorities recently called upon domestic chip manufacturers such as Huawei and Cambricon, along with Alibaba and Baidu, to examine NVIDIA chips and determined that Chinese products performed better.” It was also disclosed that last month, the CAC urged Chinese technology companies to clarify their use of NVIDIA’s H20 AI accelerator, effectively encouraging them to cease its usage.
◇Swift Increase in Chinese Semiconductor Strength
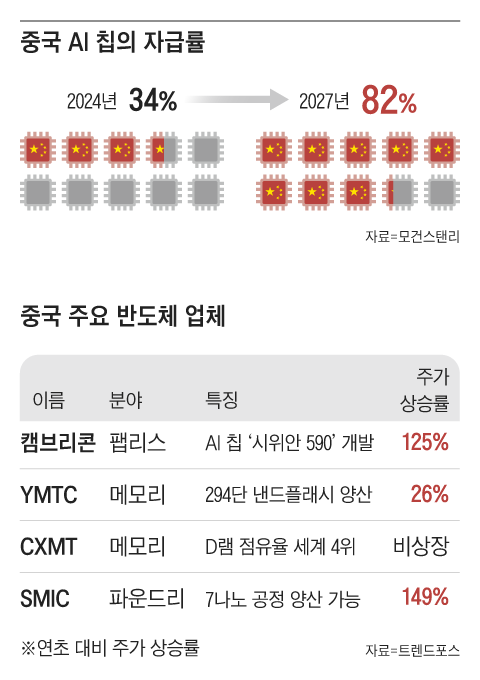
China’s semiconductor sector has developed a local ecosystem, with technological progress now matching that of the U.S., Taiwan, and South Korea. Particularly, it demonstrates strong self-reliance in the AI chip field. As per Morgan Stanley, China’s AI chip self-sufficiency rate, which stood at 34% last year, is projected to climb to 82% by 2027.
Chinese technology leaders Alibaba and Baidu have been training artificial intelligence models with self-developed chips since the beginning of this year. Huawei announced on the 18th that it plans to launch four new iterations of its Ascend AI chips within the next three years. Huawei stated, “China has successfully addressed technological barriers that had previously restricted access to South Korean and U.S. suppliers.” Cambricon, referred to as ‘China’s NVIDIA,’ experienced a 125% increase in its stock price this year while working on its own AI chips.
The semiconductor contract manufacturing industry is also experiencing rapid growth. SMIC, China’s leading foundry, intends to double its 7-nanometer (1 nanometer equals one-billionth of a meter) production capacity next year. Although it has not yet entered the advanced sub-3-nanometer processes that are currently controlled by Samsung Electronics and TSMC, it secured 5.1% of the global foundry market share in the second quarter of this year by excelling in the general-purpose foundry segment. In terms of revenue, it is closely following Samsung Electronics (with a 7.3% market share). The competition in memory semiconductors is also becoming more intense. YMTC managed to begin mass-producing 294-layer NAND flash memory in February of this year, achieving a level where it can directly compete with South Korean firms.
◇The U.S.-China Semiconductor Power Struggle Advances to a New Stage
The competition between the U.S. and China for dominance in the semiconductor industry is anticipated to move into a new stage. Ahn Ki-hyun, a former executive from the Korea Semiconductor Industry Association, remarked, “With China accelerating its domestic semiconductor development, countermeasures against the U.S. are likely to grow. It’s clear that U.S. attempts to hinder this will become stronger.” There are worries that South Korean and American companies might face challenges during this period. For NVIDIA, 16% of its overall revenue is generated from China. Lee Jong-hwan, a professor at Sangmyung University, noted, “As China strives for independence in memory semiconductors, where South Korea has a strong position, the effect on local companies will be considerable.”






Leave a comment