- Immediate concerns about H5 avian influenza approach Australia
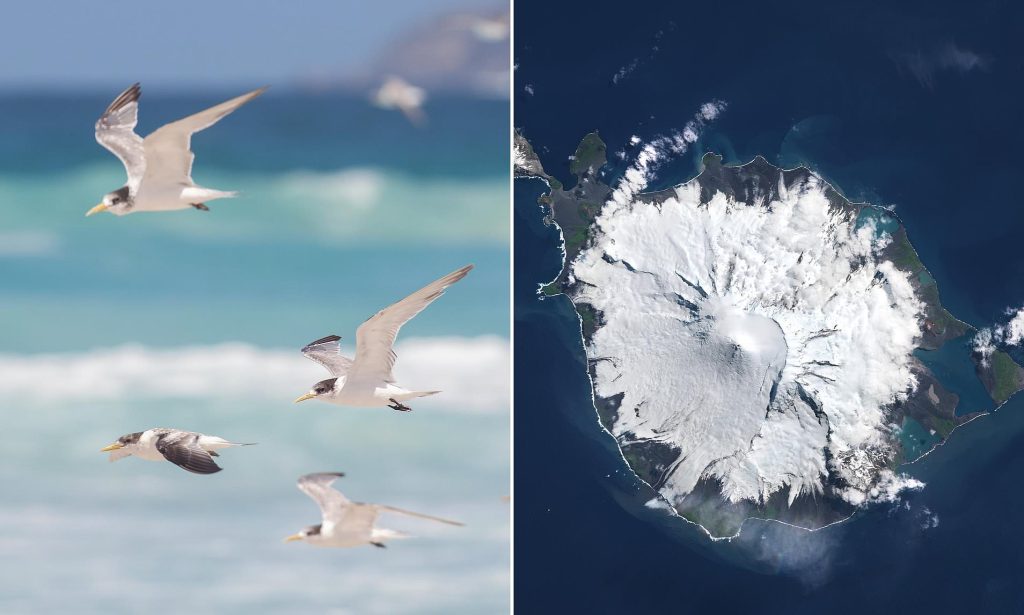
- Indicators of stress observed on the sub-Antarctic Heard Island
The initial indications of a lethalbird fluA strain has been detected on a distant Australian island, with an expert warning that its movement to the mainland is unavoidable.
Australia is now the only continent that has not been affected by the severe H5 strain of avian influenza.flu, which has become widespread, including in parts of Antarctica.
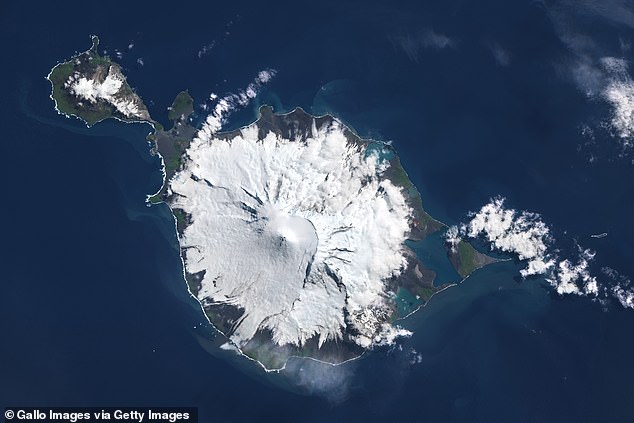
Researchers found evidence of the stress affecting sub-Antarctic Heard Island, located approximately 4000km south-west ofPerth, during a research trip.
They have recently recorded abnormal death rates among elephant seals, a species affected by H5, with additional tests planned to check if the strain is present.
“At this point, it is not a verified finding,” stated the federal environment and agriculture departments in a release on Friday.
It emphasizes the importance of Australia staying concentrated on getting ready for a potential outbreak.
A verified observation at Heard Island, located in the Southern Ocean, would not significantly raise the threat to mainland Australia, according to the department.
However, a bird flu expert stated that the presence of the strain in mainland Australia is highly likely due to its worldwide spread and could be transmitted by species found in the sub-Antarctic region.

The virus has caused the deaths of millions of birds across the globe, along with elephant seals and fur seals in Antarctica.
“It is turning out to be a multi-faceted challenge since we haven’t discovered an effective method to manage it,” said Michelle Wille, a senior researcher at the University of Melbourne’s Centre for Pathogen Genomics.
When it reaches mainland Australia, it will not make a different impression than what we have observed in other areas.
I anticipate witnessing severe effects on native animals and significant consequences for industries, especially the poultry sector.
The departments stated that the detection of signs indicating stress on Heard Island was not surprising, and there had been no recorded, abnormal deaths in other species.
The virus has already been detected on the French Kerguelen and Crozet sub-Antarctic islands, which are within 450km of the Heard and McDonald islands.
Seabirds that forage in sub-Antarctic regions and then head to mainland Australia might possibly carry the strain, according to Dr. Wille.
“This virus has shown us that it is capable of doing unusual things, such as traveling very long distances,” she said.
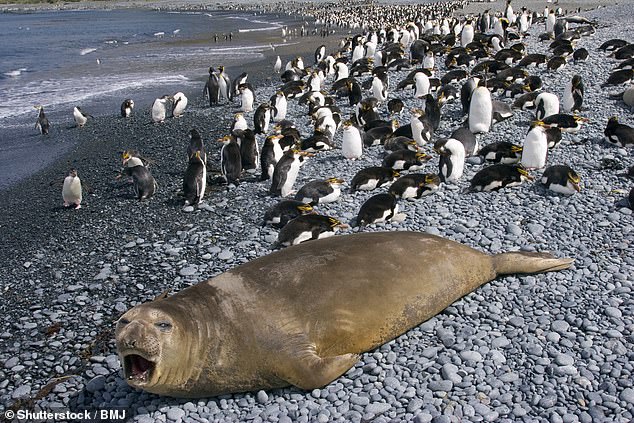


Specimens have been gathered and will undergo examination by the CSIRO once the researchers return to Australia aboard the icebreaker Nuyina in mid-November.
It is anticipated that it will require several weeks to verify the outcomes.
H5 avian influenza is a very infectious illness that has resulted in the deaths of numerous animals, such as chickens, wild birds, and other mammals.
The United States, Europe, Asia, and Antarctica have all been impacted, whereas Australia has only ever had instances of H7 – and not the H5 virus.
The Australian government is allocating over $100 million to improve bird flu readiness and boost its response capabilities.
Heard Island, listed as a World Heritage site, is characterized by UNESCO as one of the most unique and untouched island environments.
- Is Australia facing a potential bird flu crisis as the spreading H5 strain presents serious risks to both nature and farming?
- Can Australia protect itself from the approaching danger of the lethal H5N1 avian influenza virus?
- Is the globe facing a severe avian influenza outbreak caused by the H5N1 virus? Learn about the alerts from specialists and the possible effects on worldwide public health.
- Is Australia’s egg production nearing a crisis due to avian influenza affecting Victoria’s thriving agricultural sector?
- Is Australia facing a potential major flu season after Easter, with a rise in cases impacting millions?






Leave a comment